Table of Contents
What is Overclocking?
Overclocking is the process of increasing the clock speed of a computer’s CPU or GPU beyond the manufacturer’s recommended maximum. This is done to achieve better overall performance and speed up the computer’s processing power.
When a CPU or GPU is overclocked, it runs at a higher clock speed than it was designed to, which means it can perform more operations per second. This results in faster processing times and improved performance, especially when running demanding applications or playing graphics-intensive games.
Overclocking is not without its risks, however. Pushing a CPU or GPU beyond its recommended limits can cause it to overheat, which can lead to damage or even failure. It can also cause stability issues or crashes and may void the manufacturer’s warranty.
To overclock a CPU or GPU, users typically adjust the clock speed and voltage settings in their computer’s BIOS or use overclocking software tools. It’s important to note that not all CPUs and GPUs are capable of being overclocked, and those that are may have different limits and requirements for safe overclocking.
Why Overclock?

Overclocking your CPU and GPU can provide several benefits, including improved performance and faster processing speeds. By increasing the clock speed of your processor, you can complete more instructions per second, leading to a faster and more responsive computer. Here are a few reasons why you might want to consider overclocking:
Increased Performance
The most obvious benefit of overclocking is the increase in performance. Overclocking your CPU and GPU can provide a noticeable boost in performance, allowing you to run demanding applications and games more smoothly. By increasing the clock speed of your processor, you can achieve higher frame rates, faster load times, and better overall performance.
Cost Savings
Overclocking can also be a cost-effective way to improve your computer’s performance. Instead of buying a new CPU or GPU, you can simply overclock your existing hardware to achieve better performance. This can be especially useful if you’re on a tight budget and can’t afford to upgrade to the latest and greatest hardware.
Customization
Overclocking also provides an opportunity for customization. By tweaking your CPU and GPU settings, you can achieve a more personalized computing experience. For example, you can adjust the clock speed to prioritize certain tasks, such as gaming or video editing. This level of customization can help you get the most out of your hardware and tailor your computer to your specific needs.
Risks and Considerations
While overclocking can provide several benefits, it’s important to note that there are also risks and considerations to keep in mind. Overclocking can put additional stress on your hardware, which can lead to higher temperatures and potential damage if not done properly. It’s important to research and follow proper overclocking techniques to minimize these risks and ensure the longevity of your hardware. Additionally, overclocking may void your warranty, so it’s important to consider this before making any changes to your hardware.
What to Expect from Overclocking #gains or losses

Overclocking your CPU and GPU can provide a noticeable performance boost, but it also comes with some risks and drawbacks. Here are some things to keep in mind when considering overclocking:
Increased Performance
The primary benefit of overclocking is increased performance. By increasing the clock speed of your CPU and GPU, you can make them complete tasks faster and more efficiently. This can result in smoother gameplay, faster rendering times, and quicker file transfers.
Increased Heat Output
One of the downsides of overclocking is increased heat output. Overclocking your CPU and GPU will cause them to generate more heat, which can lead to stability issues, crashes, and even permanent hardware damage if not managed properly.
Increased Power Consumption
Overclocking also increases the power consumption of your CPU and GPU. This means that your system will draw more power from the wall, which could result in higher electricity bills and potentially even require a higher wattage power supply.
Risk of Damage
Overclocking can be risky if not done properly. Pushing your CPU and GPU beyond their recommended limits can cause permanent damage to the hardware. It’s important to research your specific hardware and follow best practices for overclocking to minimize the risk of damage.
Noise and Cooling
Overclocking can also result in increased noise levels from your system’s fans as they work harder to dissipate the extra heat generated by the overclocked components. It’s important to ensure that your system has adequate cooling to handle the increased heat output and prevent overheating.
Overclocking can provide a performance boost for your CPU and GPU, but it’s important to weigh the risks and drawbacks before attempting it. With proper research and best practices, overclocking can be a safe and effective way to get more out of your hardware.
Risks of Overclocking

Overclocking your CPU and GPU can improve your PC’s performance, but it also comes with risks. Here are some of the potential risks of overclocking:
1. Reduced Lifespan
Overclocking can cause your CPU and GPU to run at higher temperatures, which can reduce their lifespan. Higher temperatures can also cause damage to other components in your PC, such as your motherboard and RAM.
2. Stability Issues
Overclocking can cause stability issues, such as system crashes and freezes. This can be especially problematic if you’re using your PC for work or other important tasks.
3. Voiding Warranties
Overclocking can void the warranty on your CPU and GPU. This means that if anything goes wrong with your components, you won’t be able to get them repaired or replaced under warranty.
4. Data Loss
Overclocking can cause data loss if your system crashes or freezes. This can be especially problematic if you’re working on important documents or files.
5. Increased Power Consumption
Overclocking can increase the power consumption of your PC, which can lead to higher electricity bills. It can also put more strain on your power supply, which can cause it to fail.
It’s a great way to improve your PC’s performance, but it’s important to be aware of the risks involved. If you do decide to overclock, make sure you do it carefully and monitor your system’s temperature and stability.
Overclocking Your CPU
What to Know Before Overclocking Your CPU
Now that you have an idea of what overclocking can provide in terms of raw performance and the associated drawbacks. So Before diving into overclocking your CPU, there are a few things to consider. Overclocking can increase your CPU’s performance, but it can also cause damage if done incorrectly. It’s important to understand the risks involved and take precautions to avoid damaging your CPU.
One thing to keep in mind is that not all CPUs are created equal. Some CPUs are better suited for overclocking than others. It’s important to research your specific CPU model to understand its potential for overclocking.
Another important consideration is cooling. Overclocking can cause your CPU to generate more heat, which can damage the CPU if it gets too hot. It’s important to have adequate cooling in place to prevent overheating.
How to Overclock Your CPU
To overclock your CPU, you will need to adjust the CPU multiplier and voltage settings in your computer’s BIOS. The CPU multiplier determines the frequency at which the CPU runs, while the voltage settings determine the amount of power the CPU receives.
It’s important to note that overclocking can void your CPU’s warranty, so proceed with caution. It’s also important to make small adjustments and test your system’s stability after each adjustment to avoid damaging your CPU.
Common Overclocking Tools
There are several software tools available to help you overclock your CPU. Some popular options include:
- Intel Extreme Tuning Utility (Intel XTU)
- AMD Overdrive
- MSI Afterburner
- EVGA Precision X1
Tips for Overclocking Your CPU Safely
To overclock your CPU safely, consider the following tips:
- Research your specific CPU model to understand its potential for overclocking.
- Make small adjustments and test your system’s stability after each adjustment.
- Monitor your CPU’s temperature to ensure it doesn’t overheat.
- Have adequate cooling in place to prevent overheating.
- Avoid making extreme adjustments that could damage your CPU.
- Keep in mind that overclocking can void your CPU’s warranty.
Overclocking Your GPU

What to Know Before Overclocking Your GPU
Before overclocking your GPU, it’s important to understand what you’re getting into. Overclocking involves pushing your GPU beyond its original specifications, which can lead to increased performance but also comes with risks.
One of the biggest risks of overclocking is overheating, which can damage your GPU if left unchecked. Overclocking can also void your GPU’s warranty, so it’s important to weigh the potential benefits against the risks.
How to Overclock Your GPU
To overclock your GPU, you’ll need to use specialized software that allows you to adjust the clock speed and voltage of your GPU. Before you start, it’s important to benchmark your system to ensure it is stable at its out-of-the-box clock speeds.
Once you’ve established a baseline, you can start increasing the clock speed and voltage in small increments, testing your system after each change to ensure stability. It’s important to monitor your GPU’s temperature during the overclocking process to avoid overheating.
Common Overclocking Tools
There are several popular overclocking tools available, including:
- MSI Afterburner
- EVGA Precision X1
- ASUS GPU Tweak II
- Gigabyte AORUS Engine
Each of these tools provides a user-friendly interface for adjusting clock speeds, voltages, and fan speeds.
Tips for Overclocking Your GPU Safely
To overclock your GPU safely, consider the following tips:
- Start with small increments and test your system after each change
- Monitor your GPU’s temperature and adjust fan speeds as necessary
- Avoid increasing voltage too much, as this can lead to overheating and damage
- Keep an eye on your GPU’s performance and stability, and be prepared to dial back your overclocking if necessary
By following these tips and using the right tools, you can safely overclock your GPU and achieve better performance in your favorite games and applications.
Testing Your Overclock

Once you have overclocked your CPU and GPU, it is important to test the stability of your system to ensure that it can handle the increased performance. This section will cover how to test your overclock and make any necessary adjustments.
How to Test Your Overclock for Stability
The most common way to test the stability of your overclock is to use stress testing software. There are several options available, including Prime95, AIDA64, and IntelBurnTest. These programs will put a heavy load on your CPU and GPU, testing their stability under extreme conditions.
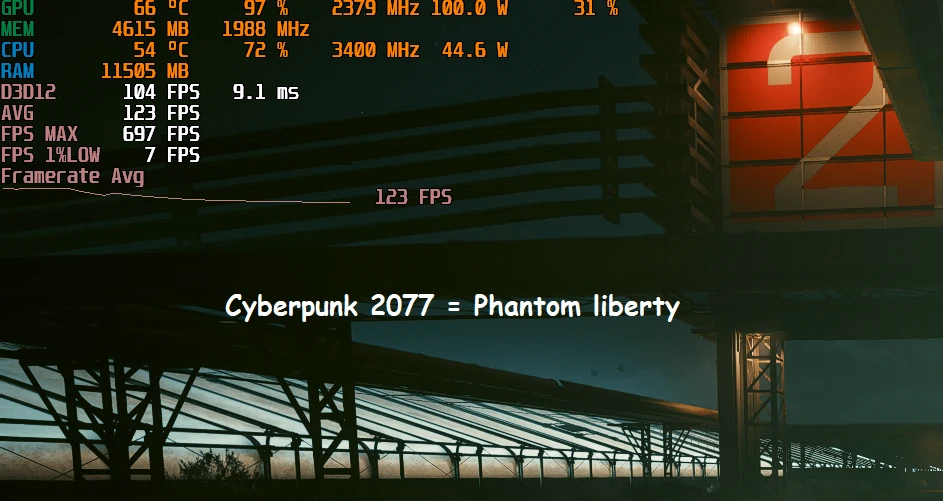
The screenshot shows that I have underclocked my non-XT variant of the RX6700 GPU to achieve optimal performance with my old Ryzen CPU. As a result, the FPS results are consistent and the power consumption is under 105w. Additionally, the temperature has decreased by 10 degrees, although this may vary depending on the GPU variant. Please disregard the MAX FPS and 1% LOW figures in this screenshot as they are abnormally high. settings i have used to underclock are attached below.
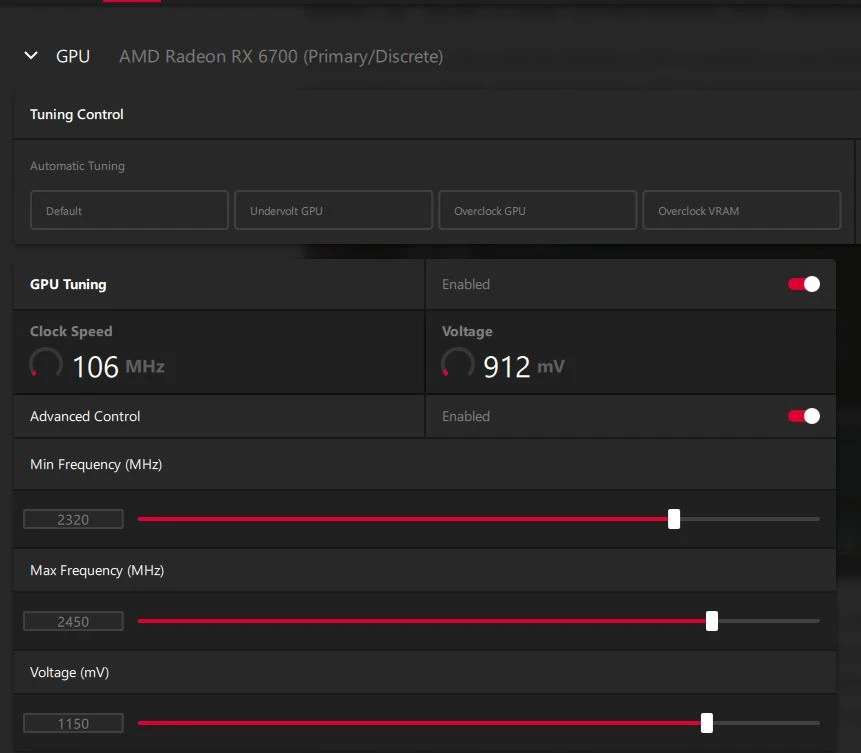
The results may vary according to your card and overall system components compatibility.
Once you have run a stress test for an extended period (at least 30 minutes), check for any errors or crashes. If your system passes the stress test without any issues, your overclock is stable and you can move on to using your system normally.
How to Adjust Your Overclock If Needed
If your system fails the stress test, you will need to adjust your overclock to make it more stable. The first step is to decrease the clock speed of your CPU or GPU slightly and run the stress test again. Repeat this process until your system passes the stress test without any issues.
If decreasing the clock speed does not work, you may need to increase the voltage to your CPU or GPU. This will increase the power going to your components, allowing them to handle higher clock speeds. However, increasing the voltage also increases the temperature of your components, so it is important to monitor the temperature closely.
Overall, testing the stability of your overclock is an important step to ensure that your system can handle the increased performance. By following these steps, you can ensure that your system is stable and running at its maximum potential.